Introduction
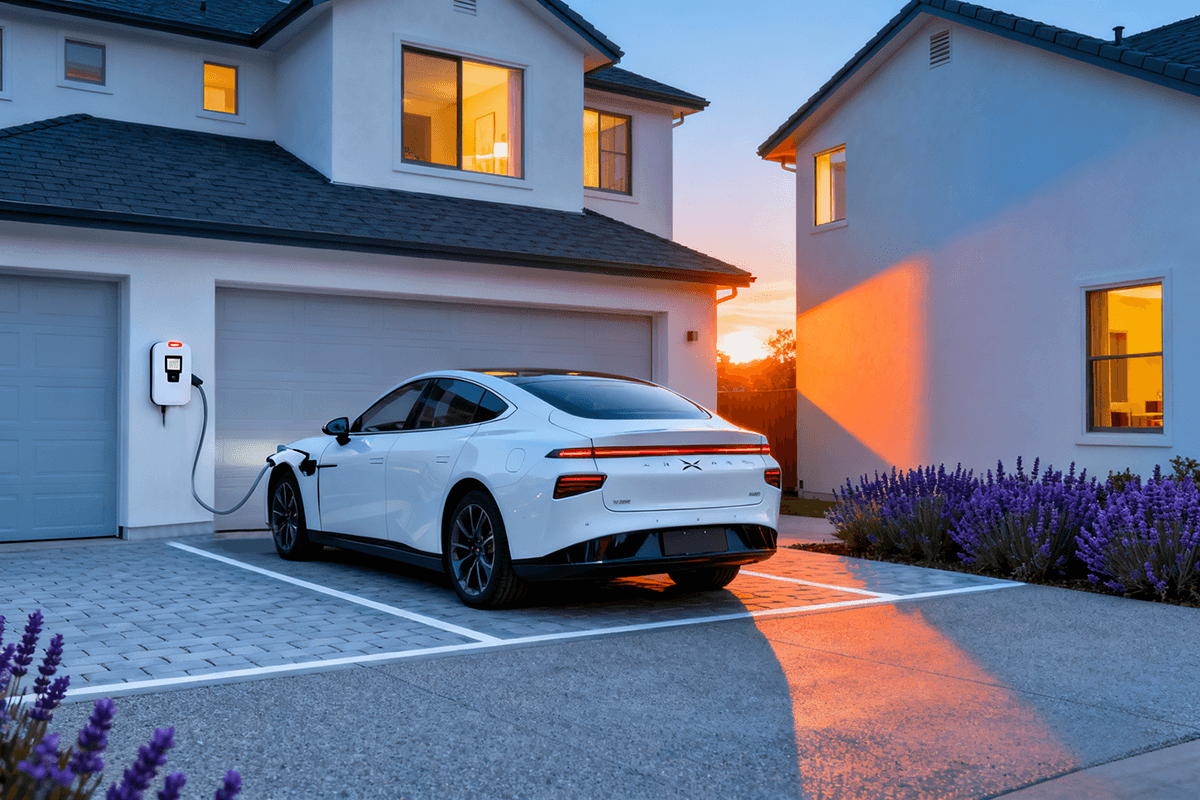
With the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), home charging stations have become an essential part of the daily lives of EV owners. As an important component of home charging infrastructure, home charging stations not only provide convenient charging experiences but also greatly enhance the efficiency and convenience of using electric vehicles. This article will discuss the different types of home charging stations, installation requirements, and selection points to help consumers better understand how to choose the right charging equipment for their home needs.
1. Types and Features of Home Charging Stations
For home users, choosing the right charging station is not only about meeting daily charging needs but also considering charging speed, ease of installation, and safety.
1.1 7kW Type 2 Charging Stations
7kW Type 2 charging stations are the most common configuration for home use, utilizing AC charging technology to charge EVs through the home power system at a moderate speed.
This charger is compatible with most commonly used EVs on the market, especially those that use the Type 2 connector, offering a stable and cost-effective charging experience.
For charging stations 7kW Type 2, the existing home electrical load can easily support the charging station, requiring no large-scale modifications to the power grid and easy installation.
1.2 Level 2 EV Chargers
Level 2 EV Chargers typically provide higher charging power, allowing for faster charging compared to standard home outlets.
It is suitable for most residential areas, especially those that need a faster charging speed.
This type of charger requires a dedicated circuit for installation and typically requires a licensed electrician, but the increase in charging speed makes it a popular choice for many households.
1.3 Charging Stations with Type B RCD
Charging stations with Type B RCD (Residual Current Device) provide effective protection against electrical faults during charging, ensuring safety.
Type B RCDs have a higher ability to detect DC leakage, which is especially important when installing DC chargers for EVs to ensure additional electrical safety protection.
2. Installation Requirements for Home Charging Stations
When selecting and installing a home charging station, users need to ensure that the following basic requirements are met:
2.1 Electrical Supply and Wiring
Home charging stations typically require a dedicated circuit for installation, especially for Level 2 chargers, which need sufficient electrical current.
A licensed electrician should install the necessary wiring and circuit breakers according to the power requirements of the EV charger.
2.2 Space and Location
Wall-mounted EV Chargers are very popular for home use because they take up minimal space, are easy to install, and are perfect for most home garages and parking spaces.
When choosing the installation location for the charger, it’s important to ensure that the charger is placed in a safe and convenient spot, close enough to the EV while avoiding long wiring runs that can reduce charging efficiency.
2.3 Safety Features
When selecting a home charging station, safety is paramount. Charging stations with Type B RCD ensure that leakage currents are safely detected, and the system will shut down in case of electrical faults, protecting both the EV and the home electrical system.
3. DC Chargers for Home Use
Although DC chargers for EVs are typically used in public charging stations, they have recently started entering the home market. Their main advantage is fast charging, capable of charging the vehicle in a short amount of time. However, compared to AC chargers, they are more complex to install and cost more.
3.1 Advantages of DC Chargers for Home Use
Charging Speed: DC chargers provide power levels up to 100kW or more, making them much faster than Level 2 chargers, significantly reducing charging time.
Large Capacity Batteries: For EV owners with large battery capacities, DC charger EV can greatly reduce charging time, especially for long-distance travelers.
3.2 Challenges of DC Chargers for Home Use
High Power Demand: DC chargers require higher power from the home grid, which often needs significant upgrades for compatibility.
High Installation Costs: Compared to AC chargers, DC chargers for home use are more expensive in both equipment cost and installation.
4. Conclusion
With the growing adoption of electric vehicles, home charging stations are becoming increasingly necessary. Whether you choose 7kW Type 2, Level 2 EV chargers, or DC charger EV for home use, it is essential to select the right equipment based on your charging needs, home electrical capacity, and available space. Safety and proper installation are equally important, and opting for devices with Type B RCD will enhance the safety of the charging process.

Оставить комментарий
Все комментарии перед публикацией проверяются.
Этот веб-сайт защищается hCaptcha. Применяются Политика конфиденциальности и Условия использования hCaptcha.